Carbon Capture Industry Outlook for 2023-2030
Insights into the expected growth of the carbon capture industry and the anticipated growth in production capacity
From Carbon Footprints to Carbon Profits
Investors are pouring billions of dollars into carbon capture projects, however, it’s not due to the recognition of the importance of carbon capture technology in reducing greenhouse gases. Instead, it’s likely caused by a recent range of economic and environmental incentives offered, which many countries are now implementing to encourage investment in this area.
One such incentive can be seen is section 45Q of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, also known as the "IRA” bill that was updated in 2022. The law has major future implications for carbon markets and is expected to grow the industry from 2023-2030.
45Q Incentives
The recent increase in incentives provided by the 45Q tax credit has been a major driver of the surge in investment in carbon capture projects.
One of the key areas where these incentives have been increased is in the storage of carbon dioxide in saline geologic formations. For industrial and power generation facilities, the incentive for storing carbon dioxide in saline geologic formations has been increased from $50 to $85 per tonne, a 70% increase. For storage from Direct Air Capture (DAC) in saline geologic formations, the incentive has been increased from $50 to an impressive $180 per tonne, representing the biggest percentage increase at 260%.
Another area where incentives have been increased is in carbon capture utilization. The incentive for carbon capture utilization for Industrial and power generation has been increased from $35 to $60 per tonne, providing a 71% boost. For utilization from DAC, the incentive has been increased from $50 to $130 per tonne, representing the second biggest increase at 160%.
These incentives can be realized over a 12-year period starting from when the equipment is placed in service, providing a stable and predictable source of revenue for investors. Additionally, the fact that these credits will be inflation adjusted in 2027 and indexed to the year 2025 provides additional security for investors, emphasizing the inflation hedge characteristics of investing in carbon markets. Overall, the increase in incentives provided by the 45Q tax credit can be credited as a significant driver of the recent surge in investment in carbon capture projects further described below.
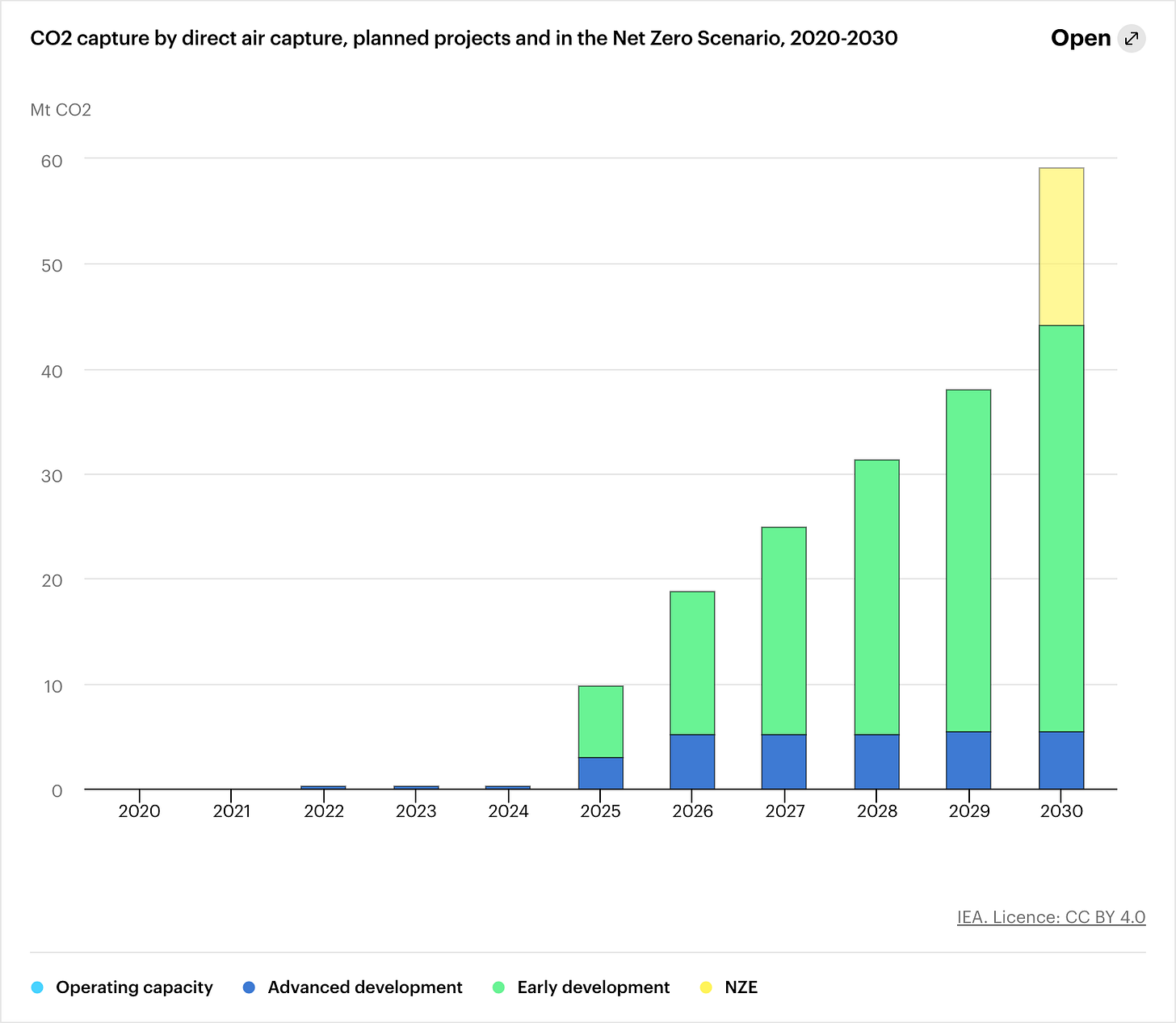
Small-Scale Present, Big-Scale Future
(Graph Source: IEA)
Currently, only 18 DAC plants are operating in the U.S, Europe, and Canada, and these are small-scale projects capturing a relatively minuscule amount of CO2 compared to the scale of greenhouse gas emissions. Most of these plants are being operated for testing and demonstration purposes, reflecting the new technology's infancy stage and the lack of economies of scale to drive down costs. However, plans are in place to rapidly expand DAC capacity from 2025-2030, supported by an improved investment environment through government policy, such as the 45Q upgrades to incentives.
The world's first million-tonne direct air capture plant is expected to be operating in the U.S by the mid-2020s, financed by 1PointFive, created by Oxy Low Carbon Ventures (OLCV). This landmark project will capture 1 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year, located in the Permian Basin and connected to the existing CO2 pipeline network. 1PointFive plans to develop 70+ large-scale DAC facilities by 2035, each with a capacity of over a million tonnes per year.
Other major DAC projects, including the Storegga Dreamcather Project in the UK, the HIF Haru One eFuels Pilot Plant in Chile, and the Norsk e-Fuel AS consortium in Norway, are also set to come online in the mid-2020s. Despite the small capacity of DAC plants in 2023, the rapid expansion plans and major projects coming online soon indicate the technology's growing importance in the fight against climate change.
In conclusion, the recent surge in investment in carbon capture projects can be attributed to the range of economic and environmental incentives offered in the increased 45Q tax credit. These incentives have provided a stable and predictable source of revenue for investors, attracting billions of dollars in investment. The incentives have particularly targeted the storage and utilization of carbon dioxide, leading to an increase in the number of small-scale direct air capture plants for testing and demonstration purposes. However, with plans for large-scale DAC plants in the near future, the potential for carbon capture technology to reduce greenhouse gases is becoming increasingly promising.