Best Carbon Credit Stocks for 2023
Discover The Top Carbon Credit Stocks to Invest in 2023 and Benefit from the Growth of the Low-Carbon Economy
Check out our website here, and check out our carbon pricing dashboard.
New to Carbon Credits? Read here first 👇
Climate change is one of the biggest challenges facing the world today. The increasing levels of greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to global warming, which is having a detrimental impact on the environment, wildlife and human populations. As such, it is essential that we all take steps to reduce our carbon footprint and promote sustainability. One way to do this is by investing in carbon credits and allowances.
Carbon credits and allowances are units of measurement for greenhouse gas emissions. They represent the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other pollutants into the atmosphere. Companies, governments and individuals can purchase these credits and allowances as a way to offset their emissions and reduce their environmental impact.
There are several benefits to investing in carbon credits and allowances. Firstly, they provide a way for companies and individuals to offset their emissions and reduce their carbon footprint. This not only helps to mitigate the effects of climate change but also demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, which can be beneficial for brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Additionally, carbon credits and allowances are tradable commodities. This means that they can be bought and sold on the open market, providing investors with the opportunity to make a profit while promoting sustainability. As more and more companies and governments look to reduce their carbon footprint, demand for carbon credits and allowances is expected to increase, making them a potentially profitable investment opportunity.
Investing in carbon credits and allowances is also a way to support the development of clean energy technologies. By reducing the demand for fossil fuels, investment in these credits and allowances can drive innovation and help to create a more sustainable energy future. This not only benefits the environment but can also help to create new job opportunities and stimulate economic growth.
Furthermore, investing in carbon credits and allowances is a way to support the transition to a low-carbon economy. The Paris Agreement, signed by more than 190 countries, aims to keep global temperature rises below 2°C and pursue efforts to limit them to 1.5°C. To achieve this goal, countries need to transition to a low-carbon economy, which will require significant investment in clean energy and carbon-reducing technologies. By investing in carbon credits and allowances, individuals and companies can play a role in this transition and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Why Invest in Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits are becoming increasingly popular as a means of mitigating the effects of climate change and promoting sustainability. As more and more companies and governments look to reduce their carbon footprint, the demand for carbon credits is growing, making them a potentially profitable investment opportunity.
With the world transitioning towards a low-carbon economy, investing in carbon credits now is a smart move for investors looking to capitalize on the upward trend. By investing in carbon credits, investors not only have the opportunity to make a profit, but also play a role in creating a more sustainable future for us all.
With the right strategy, investing in carbon credits can be a lucrative and socially responsible investment
What are the different types of Carbon Credits?
There are several different types of carbon credits available, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits
1. Compliance Carbon Credits: These credits are used to meet mandatory emissions reductions targets set by government regulations, such as the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). Companies covered by these regulations must either reduce their emissions or purchase compliance carbon credits to offset any excess emissions.
2. Voluntary Carbon Credits: Unlike compliance carbon credits, voluntary carbon credits are not tied to mandatory emissions reductions targets. Instead, they are purchased voluntarily by companies, governments, or individuals as a way to offset their emissions and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
3. Project-Based Carbon Credits: Project-based carbon credits are generated through the development of clean energy or carbon-reducing projects, such as renewable energy projects, energy-efficient building retrofits, or reforestation projects. These credits can be sold to offset emissions generated elsewhere.
4. Certified Emission Reduction (CER) Credits: CER credits are generated through clean energy and carbon-reducing projects in developing countries and are verified by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). They can be traded and sold on the international market, providing a way for developing countries to earn revenue while reducing their carbon footprint.
5. Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) Credits: VCS credits are generated through a range of carbon-reducing projects and are verified by the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) organization. VCS credits provide a way for companies and individuals to offset their emissions and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
The Carbon Marketplace: Understanding Cap and Trade and Voluntary Systems
The carbon marketplace is a system that allows companies, governments, and individuals to buy and sell carbon credits as a means of offsetting their greenhouse gas emissions. The carbon marketplace is an important tool for reducing global emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change. There are two main types of carbon markets: cap and trade systems and voluntary systems.
Cap and Trade Systems: Cap and trade systems are mandatory emissions reduction programs that set a limit, or cap, on the amount of emissions a company or industry can emit. Companies that emit less than their allocated emissions limit can sell their unused emissions allowances to companies that exceed their limit. This creates a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions and invest in clean energy technology. The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is an example of a cap and trade system.
Voluntary Systems: Voluntary carbon markets are not tied to mandatory emissions reductions targets. Instead, companies, governments, and individuals can purchase carbon credits voluntarily as a way of offsetting their emissions and demonstrating their commitment to sustainability. Voluntary carbon credits can be generated through clean energy or carbon-reducing projects, such as renewable energy projects, energy-efficient building retrofits, or reforestation projects.
Best Carbon Credit Stocks, ETFs and ETNs for 2023
#1. KRBN - KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF
Investment Strategy
The KraneShares Global Carbon Strategy ETF (KRBN) is benchmarked to IHS Markit’s Global Carbon Index, which offers broad coverage of cap-and-trade carbon allowances by tracking the most traded carbon credit futures contracts. The index introduces a new measure for hedging risk and going long the price of carbon while supporting responsible investing.
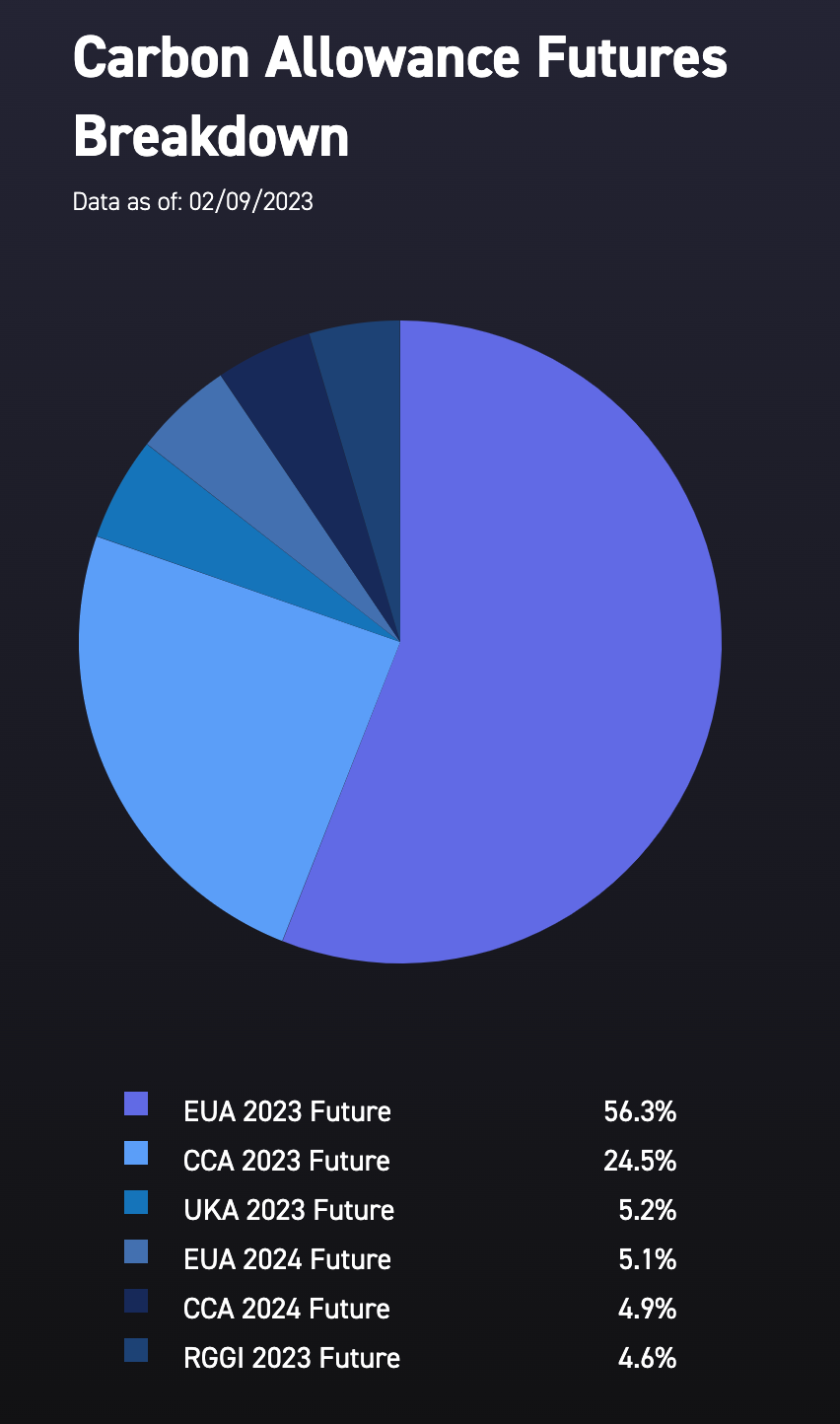
Currently, the index covers the major European and North American cap-and-trade programs: European Union Allowances (EUA), California Carbon Allowances (CCA), the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), and United Kingdom Allowances (UKA).
KRBN Highlights:
· According to IHS Markit, as of December 31, 2021 the global price of carbon was $51.45 per ton of CO2. It is estimated that carbon allowance prices need to reach $147 per ton of CO2 to meet a 1.5°C global warming limit1,2
· As of December 2021, the four largest global carbon futures markets tracked by IHS Markit’s Global Carbon Index, had an annual trading volume of $683.9 billion.1
· In April 2019, The Financial Times reported that European carbon allowances within the European Union Emissions Trading System were the world’s top-performing commodity over the past two years.3,4
· In 2021, China launched its carbon allowance market, expected to be the largest in the world, projected to cover ~3.3 billion CO2.4
#2. KEUA - KraneShares European Carbon Allowance Strategy ETF
Investment Strategy
The KraneShares European Carbon Allowance Strategy ETF (KEUA) provides targeted exposure to the European Union Allowances (EUA) cap-and-trade carbon allowance program. KEUA is benchmarked to the IHS Markit Carbon EUA Index, which tracks the most traded EUA futures contracts. As a part of the KraneShares suite of carbon ETFs, KEUA provides a new vehicle for participating in the price of carbon and hedging risk while supporting responsible investing and impact investment goals.
KEUA Highlights
· The EUA cap-and-trade program is the world's oldest and most liquid carbon allowance market. It covers approximately 40% of the EUs total emissions covering 27 EU Member States plus Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
· The program targets reducing emissions by at least 55% of 1990 levels by 2030 and climate neutrality by 2050. The "Fit for 55" package released in 2021 set out an expansion and tightening of the program, including an increased cap reduction from 2.2% to 4.2% per year.
· EUA carbon allowances are among the fastest-growing, strongest performing, and diversifying asset classes. In 2021, EU carbon allowance futures have traded around $30 billion per month.
· Can provide potential portfolio diversification due to the historically low correlation to traditional asset classes.
#3. KCCA - KraneShares California Carbon Allowance Strategy ETF
Investment Strategy:
The KraneShares California Carbon Allowance Strategy ETF (KCCA) provides targeted exposure to the California Carbon Allowances (CCA) cap-and-trade carbon allowance program. KCCA is benchmarked to the IHS Markit Carbon CCA Index, which tracks the most traded CCA futures contracts. As a part of the KraneShares suite of carbon ETFs, KCCA provides a new vehicle for participating in the price of carbon and hedging risk while supporting responsible investing and impact investment goals.
KCCA Highlights
· The CCA cap-and-trade program began in 2012, implemented by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and covers approximately 80% of the states Green House Gas (GHG) emissions. In 2014, the program was expanded to cover Quebec and its emissions.
· The program plans to reduce carbon levels to 60% of 1990 levels by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2045. The cap will reduce 4% per year to achieve this objective. Further, the program has a floor price that rises 5% plus inflation adjustment each year.
· CCA carbon allowances are among the fastest growing, strongest performing and diversifying asset classes. In 2021, CCA carbon allowance futures have traded around $1.5 billion per month.
· Can provide potential portfolio diversification due to the historically low correlation to traditional asset classes.
#4. GRN - iPath Series B Carbon ETN
GRN offers exposure to global carbon markets as represented by a Barclays index that measures the performance of emissions units—European Union Allowances (EUAs) and Certified Emission Reductions (CERs)—issued under the European Union Emission Trading Scheme and Kyoto protocol.
The index consists of all carbon futures contracts with an open interest greater than zero. Each contract is weighted by its proportional individual volume contributed to the total combined volume of all eligible contracts. The index rebalances annually on November, and exits exposure to contracts expiring in the upcoming December—rolling its exposure to futures contracts expiring in the next December.
It is worth mentioning that while the index is calculated in USD, the components are denominated in euros. Please keep in mind that this is an ETN, and not an ETF.
#5. LCTU - BlackRock U.S. Carbon Transition Readiness ETF
This ETF provides broad exposure to large- and mid-capitalization U.S. companies tilting towards those that BlackRock believes are better positioned to benefit from the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Sustainability Characteristics provide investors with specific non-traditional metrics. Alongside other metrics and information, these enable investors to evaluate funds on certain environmental, social and governance characteristics. Sustainability Characteristics do not provide an indication of current or future performance nor do they represent the potential risk and reward profile of a fund. They are provided for transparency and for information purposes only. Sustainability Characteristics should not be considered solely or in isolation, but instead are one type of information that investors may wish to consider when assessing a fund.